Clustering and Lasso Regression
1. Clustering
poke_df =
read_csv("./data/pokemon.csv") %>%
janitor::clean_names() %>%
select(hp, speed)## Parsed with column specification:
## cols(
## `#` = col_double(),
## Name = col_character(),
## `Type 1` = col_character(),
## `Type 2` = col_character(),
## Total = col_double(),
## HP = col_double(),
## Attack = col_double(),
## Defense = col_double(),
## `Sp. Atk` = col_double(),
## `Sp. Def` = col_double(),
## Speed = col_double(),
## Generation = col_double(),
## Legendary = col_logical()
## )poke_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = hp, y = speed)) +
geom_point()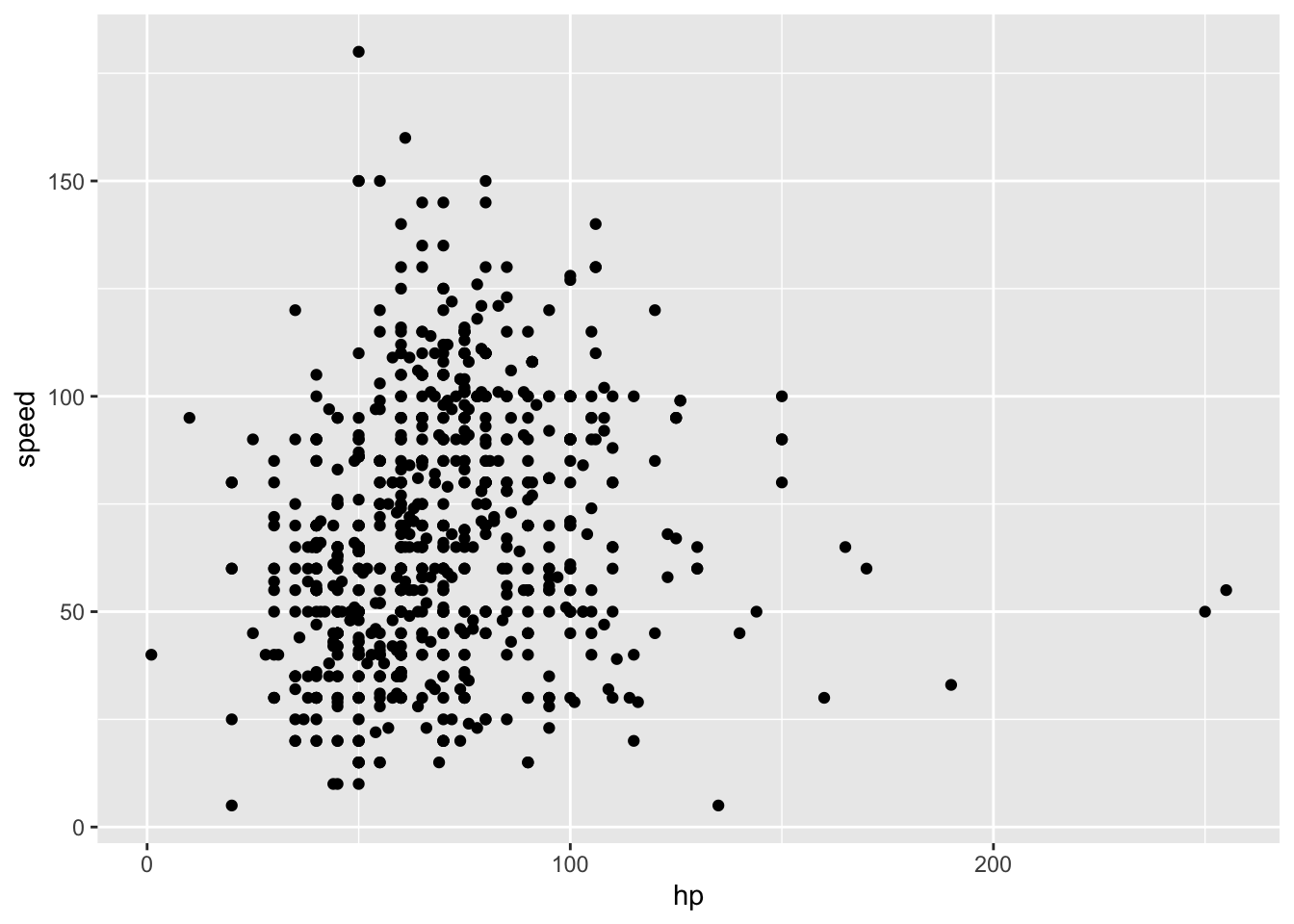
kmeans_fit =
kmeans(x = poke_df, centers = 3)poke_df =
broom::augment(kmeans_fit, poke_df)
poke_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = hp, y = speed, color = .cluster)) +
geom_point()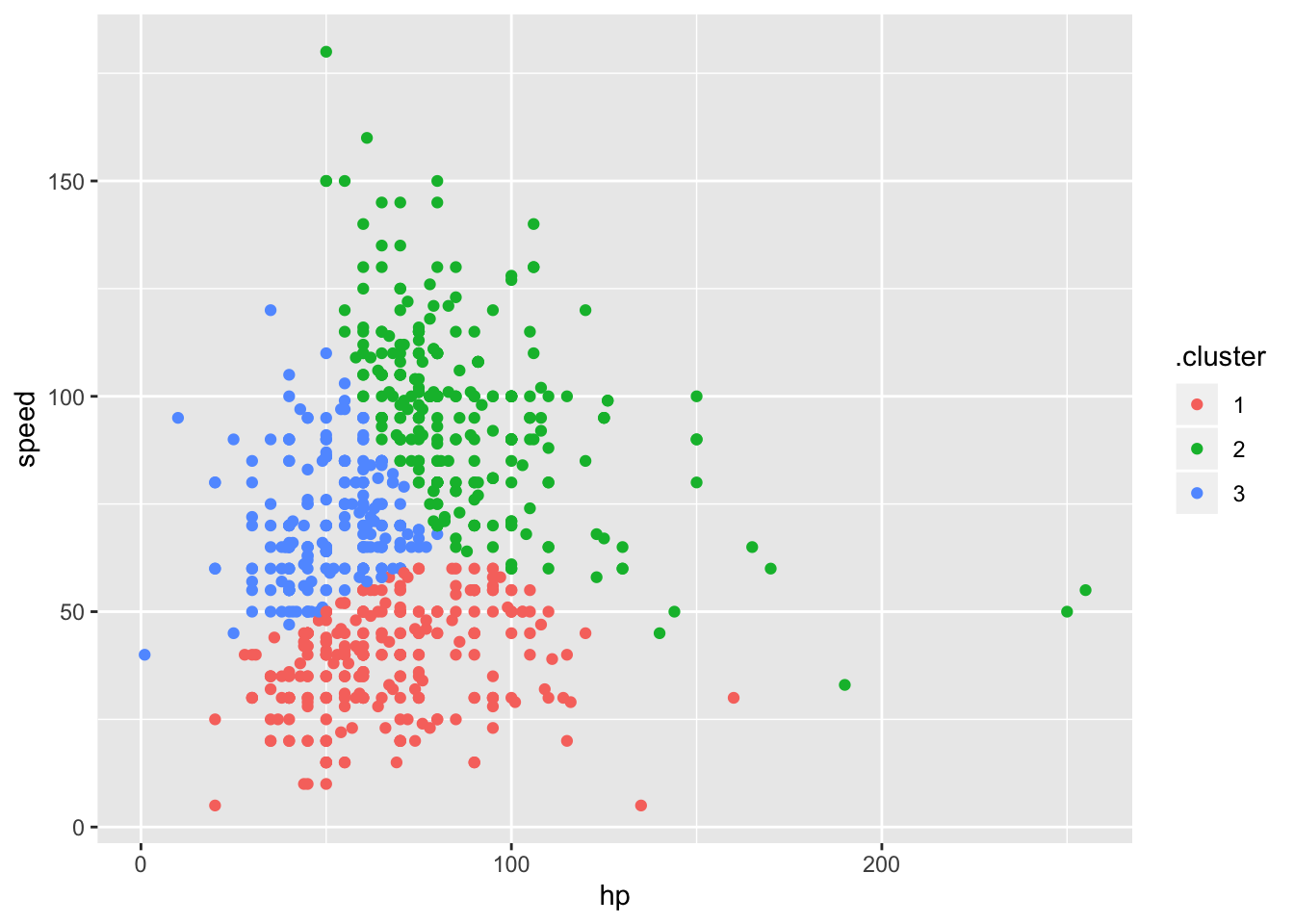
clusts =
tibble(k = 2:4) %>%
mutate(
km_fit = map(k, ~kmeans(poke_df, .x)),
augmented = map(km_fit, ~broom::augment(.x, poke_df))
)
clusts %>%
select(-km_fit) %>%
unnest(augmented) %>%
ggplot(aes(hp, speed, color = .cluster)) +
geom_point(aes(color = .cluster)) +
facet_grid(~k)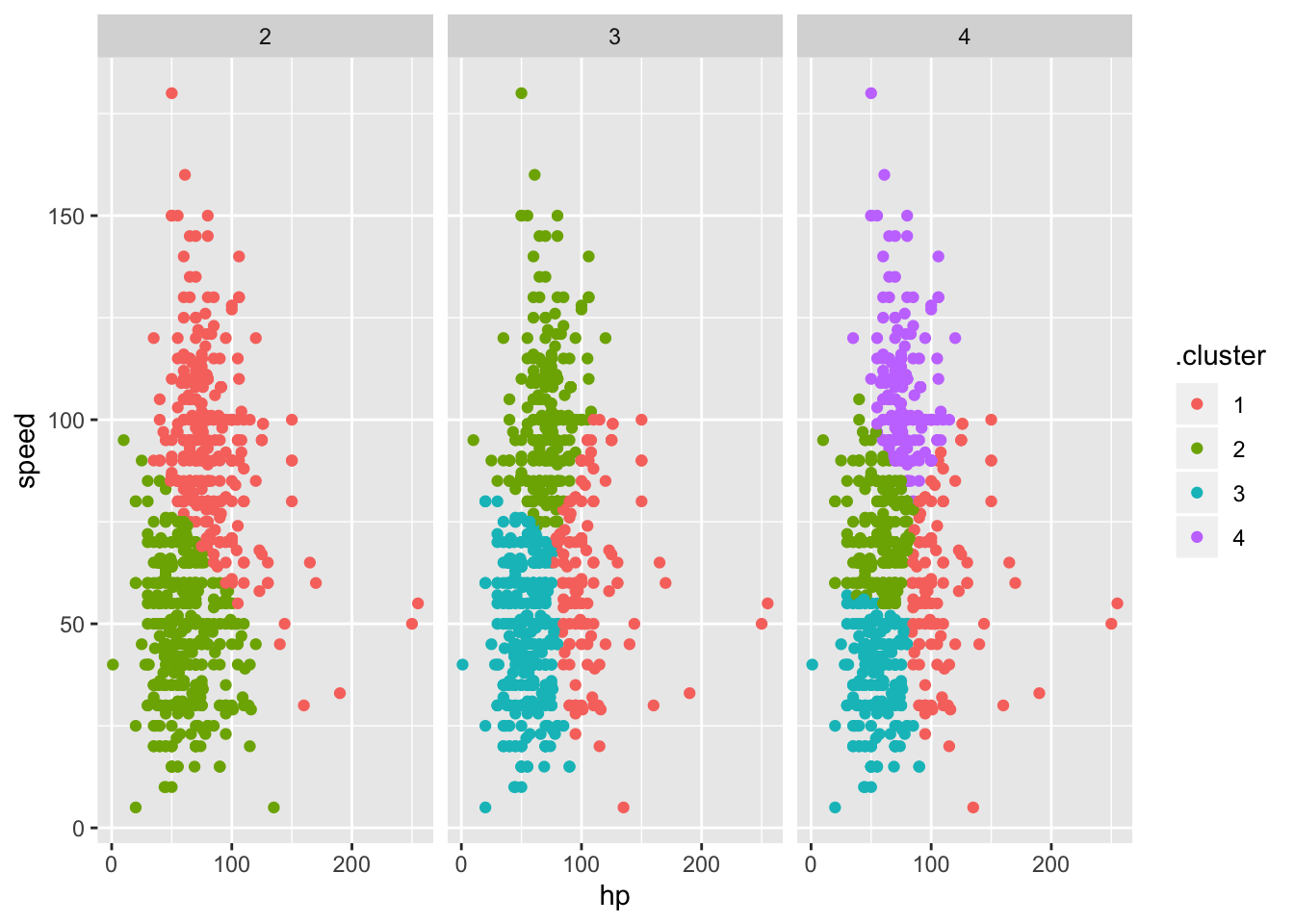
Clustering: trajectories
traj_data =
read_csv("./data/trajectories.csv")## Parsed with column specification:
## cols(
## subj = col_double(),
## week = col_double(),
## value = col_double()
## )traj_data %>%
ggplot(aes(x = week, y = value, group = subj)) +
geom_point() +
geom_path()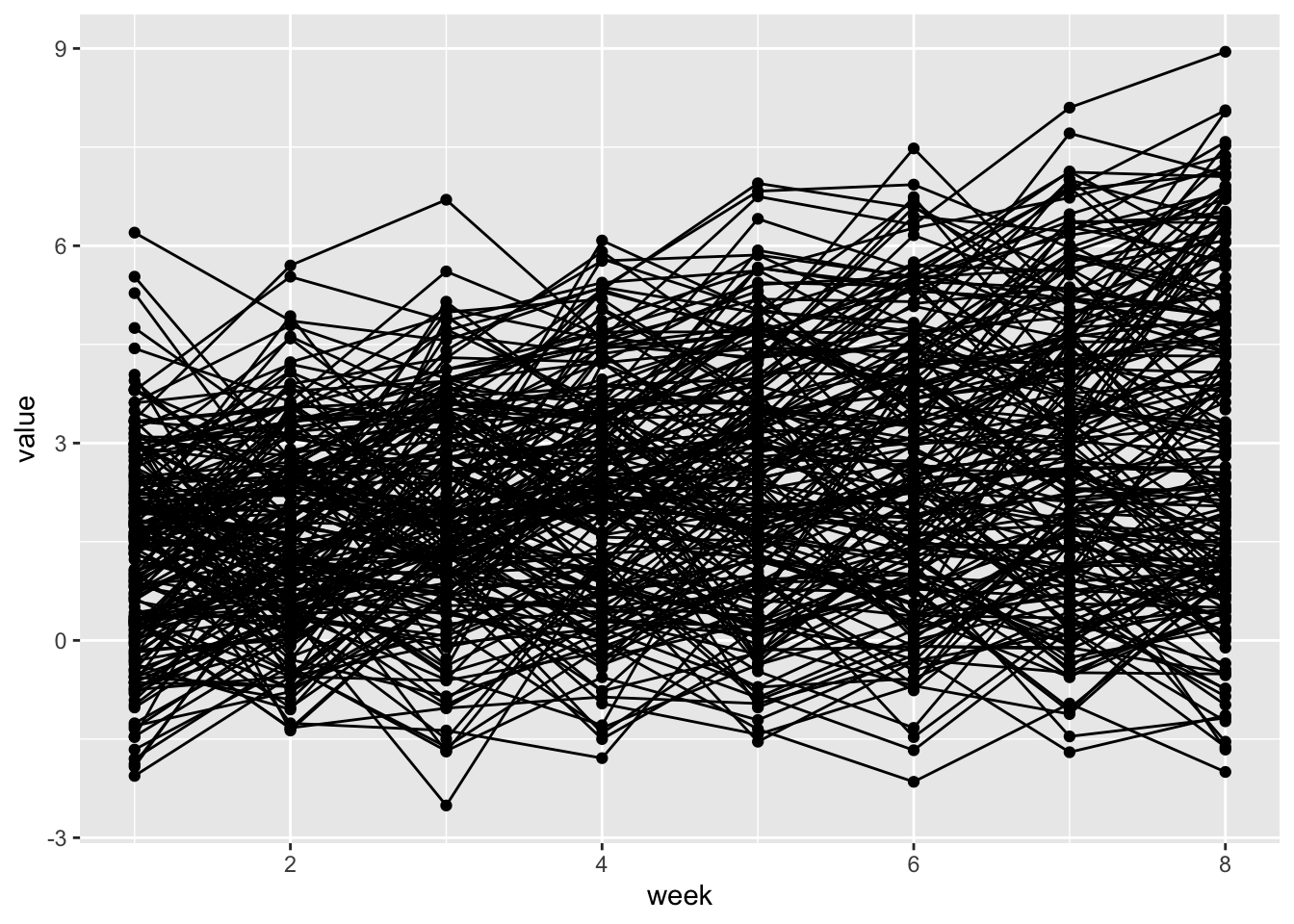
int_slope_df =
traj_data %>%
nest(data = week:value) %>%
mutate(
models = map(data, ~lm(value ~ week, data = .x)),
result = map(models, broom::tidy)
) %>%
select(subj, result) %>%
unnest(result) %>%
select(subj, term, estimate) %>%
pivot_wider(
names_from = term,
values_from = estimate
) %>%
rename(int = "(Intercept)", slope = week)int_slope_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = int, y = slope)) +
geom_point()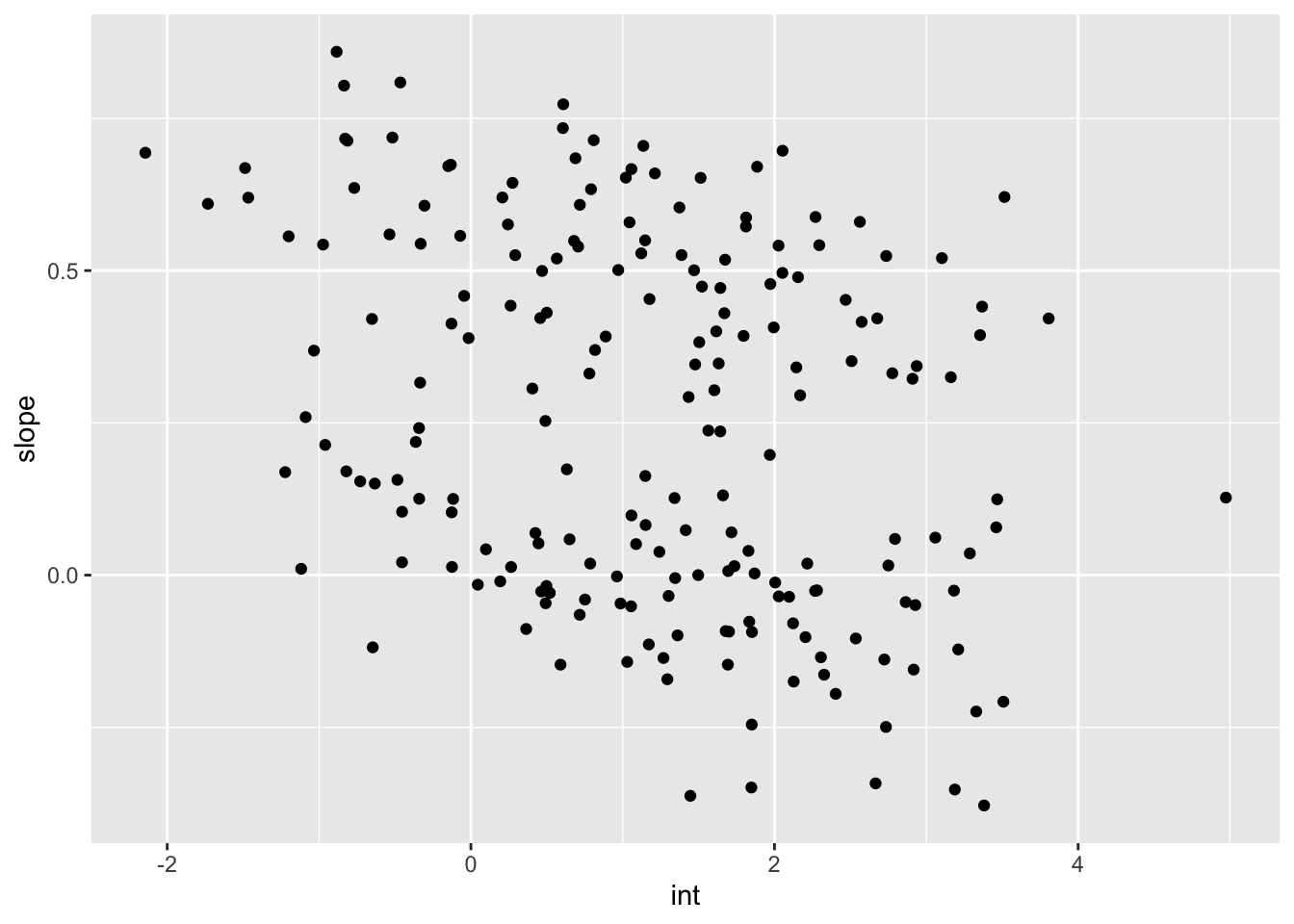
km_fit =
kmeans(
x = int_slope_df %>% select(-subj) %>% scale,
centers = 2)
int_slope_df =
broom::augment(km_fit, int_slope_df)int_slope_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = int, y = slope, color = .cluster)) +
geom_point()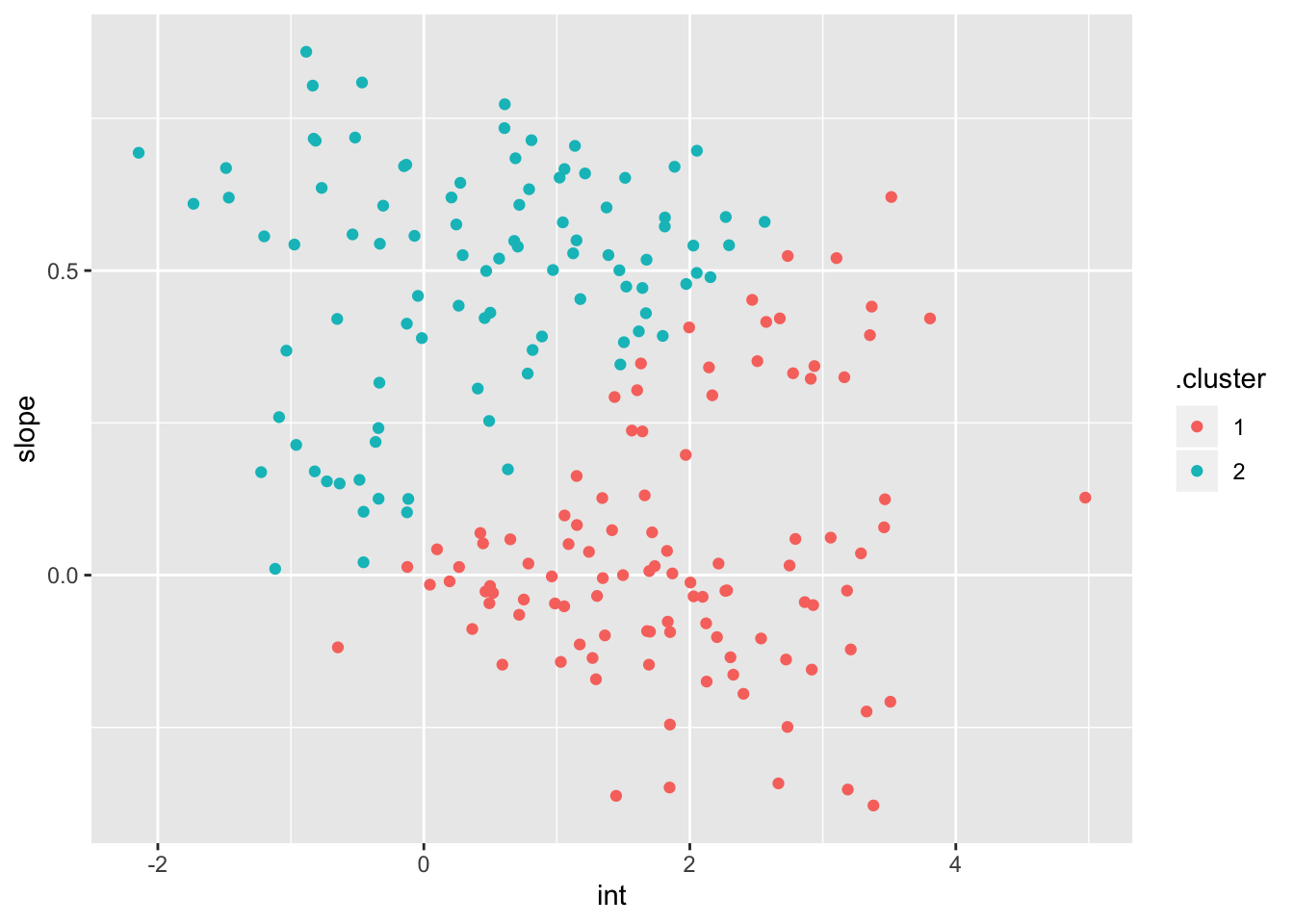
left_join(traj_data, int_slope_df) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = week, y = value, group = subj, color = .cluster)) +
geom_point() +
geom_path() ## Joining, by = "subj"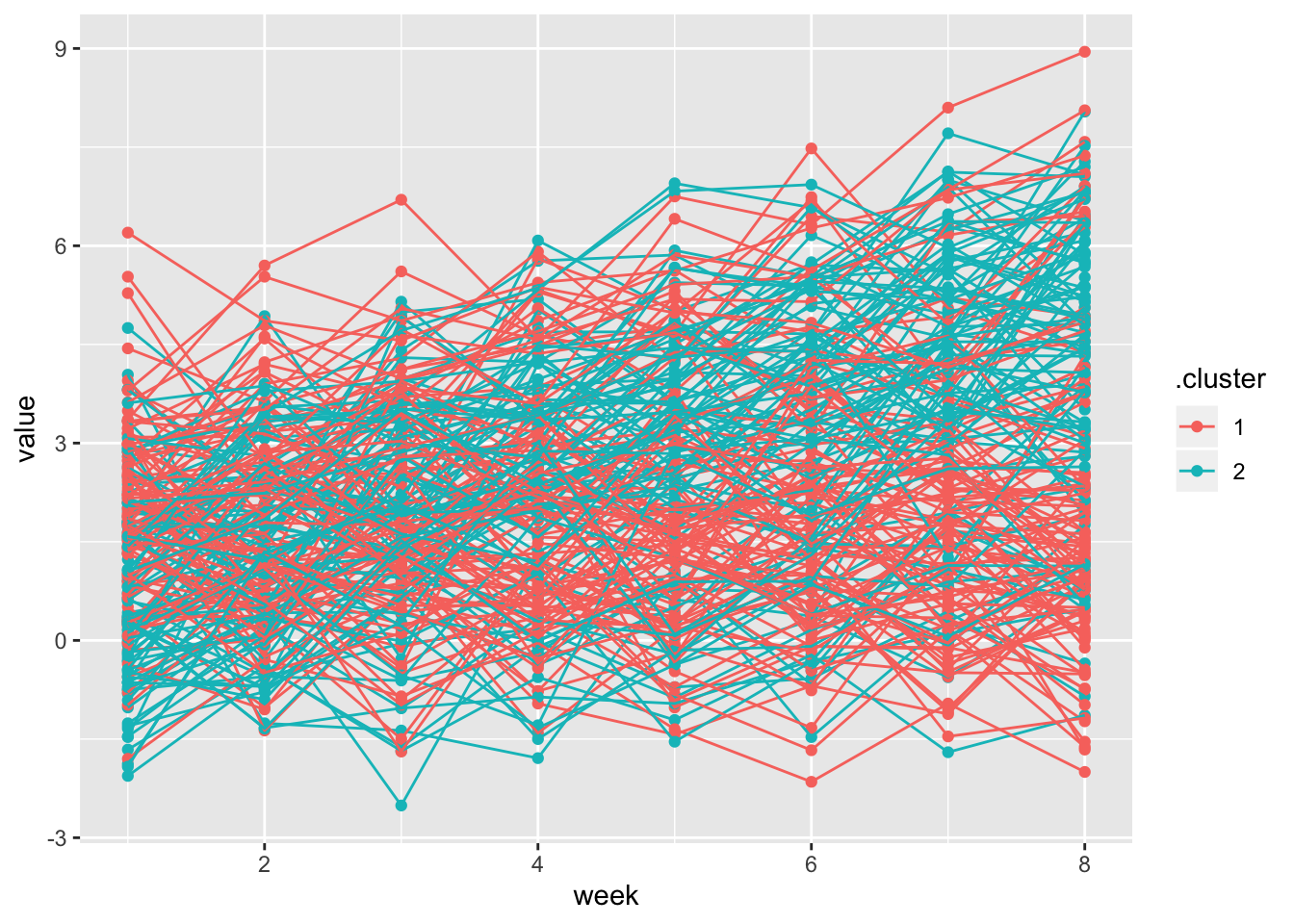
2. LASSO
bwt_df =
read_csv("./data/birthweight.csv") %>%
janitor::clean_names() %>%
mutate(
babysex = as.factor(babysex),
babysex = fct_recode(babysex, "male" = "1", "female" = "2"),
frace = as.factor(frace),
frace = fct_recode(frace, "white" = "1", "black" = "2", "asian" = "3",
"puerto rican" = "4", "other" = "8"),
malform = as.logical(malform),
mrace = as.factor(mrace),
mrace = fct_recode(mrace, "white" = "1", "black" = "2", "asian" = "3",
"puerto rican" = "4")) %>%
sample_n(200)## Parsed with column specification:
## cols(
## .default = col_double()
## )## See spec(...) for full column specifications.y = bwt_df$bwt
x = model.matrix(bwt ~ ., bwt_df)[,-1]
lambda = 10^(seq(3, -2, -0.1))
lasso_fit =
glmnet(x, y, lambda = lambda)
lasso_cv =
cv.glmnet(x, y, lambda = lambda)
lambda_opt = lasso_cv$lambda.minThe plot below shows coefficient estimates corresponding to a subset of the predictors in the dataset – these are predictors that have non-zero coefficients for at least one tuning parameter value in the pre-defined grid.
broom::tidy(lasso_fit) %>%
select(term, lambda, estimate) %>%
complete(term, lambda, fill = list(estimate = 0) ) %>%
filter(term != "(Intercept)") %>%
ggplot(aes(x = log(lambda, 10), y = estimate, group = term, color = term)) +
geom_path() +
geom_vline(xintercept = log(lambda_opt, 10), color = "blue", size = 1.2) +
theme(legend.position = "none")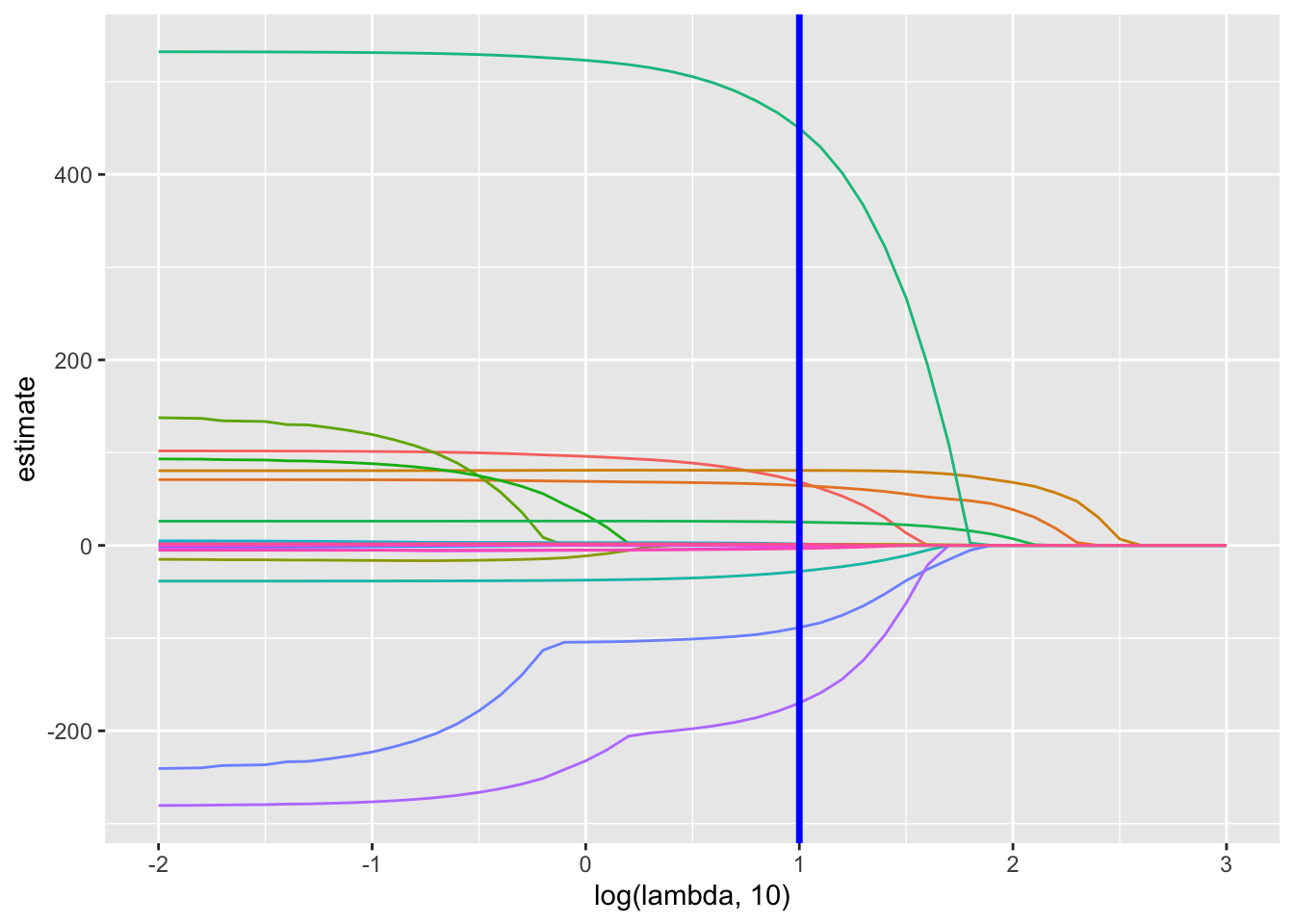
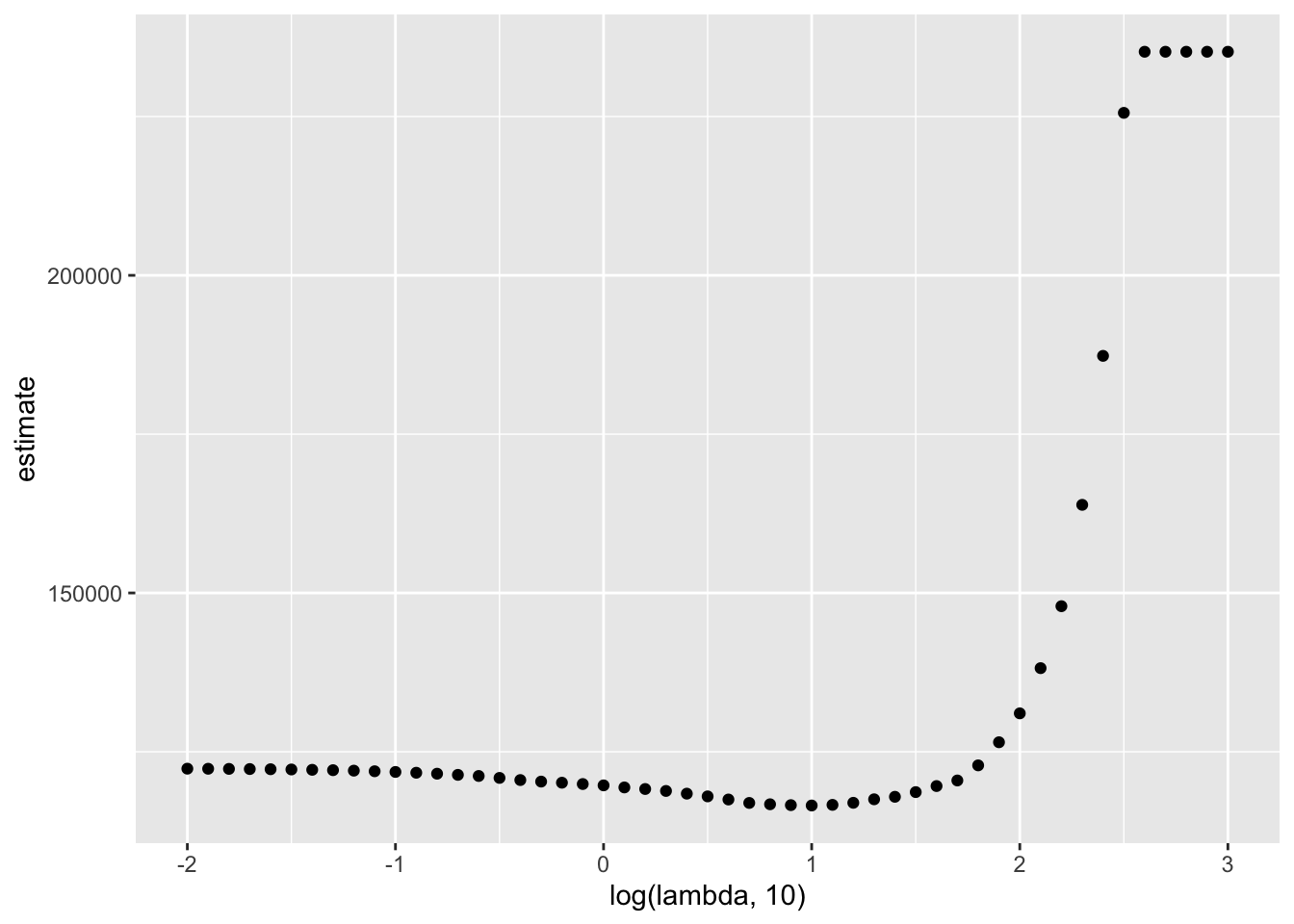
The next plot shows the CV curve itself.
broom::tidy(lasso_cv) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = log(lambda, 10), y = estimate)) +
geom_point()